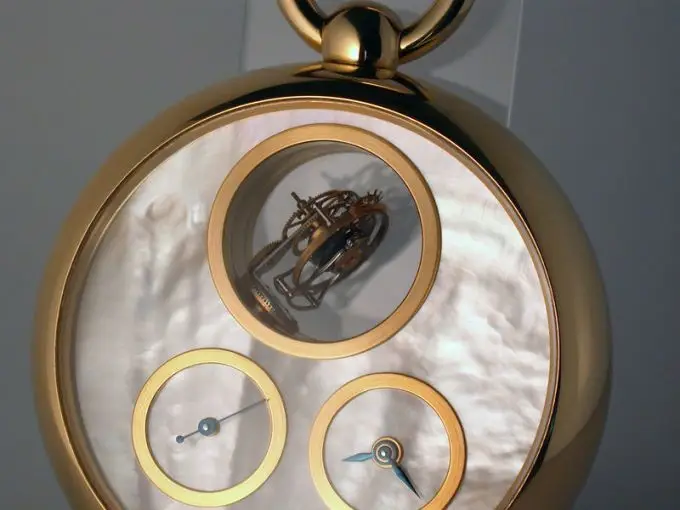

In 2003, the German watchmaker Thomas Prescher, inspired by the invention of Anthony Randall (two-axis tourbillon in a carriage clock - information below) developed for a pocket watch a two-axis flying tourbillon called gyrotourbillon, in which the second axis rotates parallel to the dial of the watch.
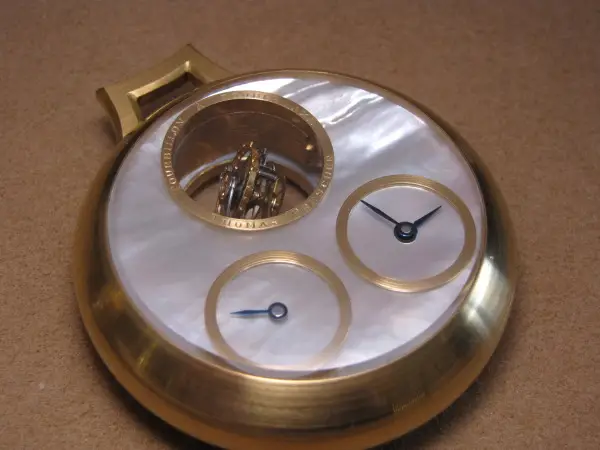

Thomas Prescher presented an updated version of the two-axis tourbillon in a wristwatch In 2004.
Also in 2004 Thomas Prescher Haute Horlogerie developed a triaxial tourbillon for wristwatch.
All watches were shown at the Baselworld exhibition in 2003 and 2004.
___
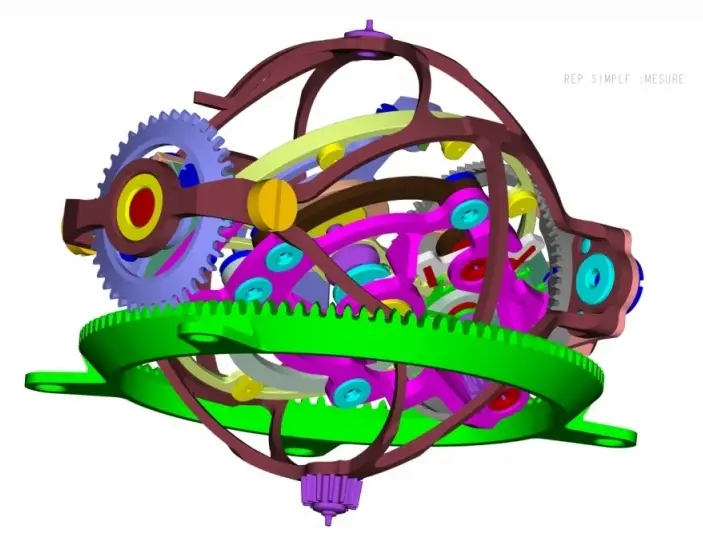
In 2004, Jaeger-LeCoultre also presented a spherical escapement device called Gyrotourbillon I. It was placed in the JLC 177 mechanism with manual winding, which was equipped with equation of time, annual calendar and 8 days power reserve.
The tourbillon was made of 90 titanium elements with a total weight of 0.336 grams. The gyrotourbillon has two cages that rotate in two surfaces. The gyrotourbillon protects six anti-shock systems.
___
In 1977, the two-axis tourbillon was patented and installed in a portable clock by Anthony Randall, who inspired Thomas Prescher to develop smaller versions of two-axis tourbillon for pocket and wristwatches.
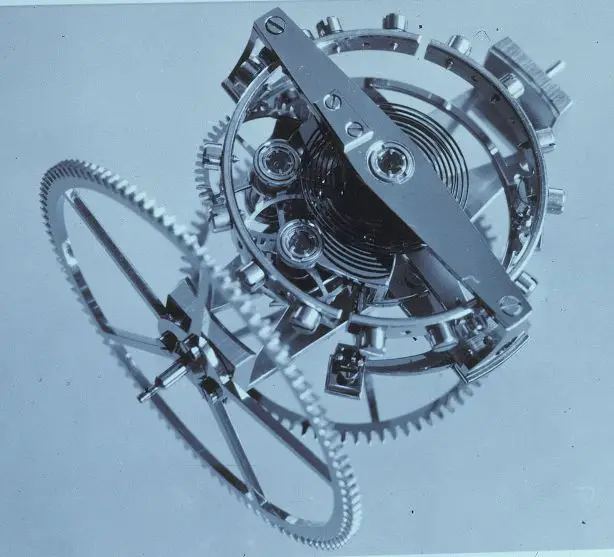
Application: Thomas Prescher
Other records: Timeline of Watchmaking Innovations














































 INSTAGRAMIE
INSTAGRAMIE









 greenlogic.eu
greenlogic.eu